A UX strategy is a plan that defines how a business intends to create a meaningful and flawless user experience for the target users of a digital product or service. An effective UX strategy helps the organization to create and operate on a shared vision of the desired state of the user experience while setting clear objectives and creating a plan to achieve them.
A UX strategy always comes on the tail of user research
With user research being the backbone of an effective UX strategy, we can ensure that we are taking a data-driven approach to the development of the product
Designing a meaningful product is one thing, but making sure this is aligned with the specific needs and goals of the business is of utmost importance for a successful UX strategy.
UX Strategy:
- Allows for scalability: UX team thinks beyond the current requirements and user behaviors. This means that the user experience of a product can be seamless throughout its different features
- Drives innovation
- Creates brand reputation
- Create a competitive advantage for the organization
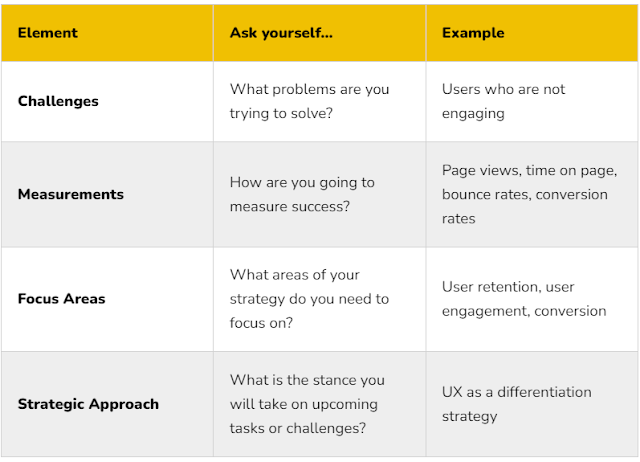
UX strategy consists of three main elements:
Vision: Desired future state of the user experience
Goals: These goals should be clear and measurable and they should be aligned with any KPIs and any UX metrics that are set by the company.
Plan: All the actions that need to be taken to meet the set goals and achieve the vision.




Comments
Post a Comment